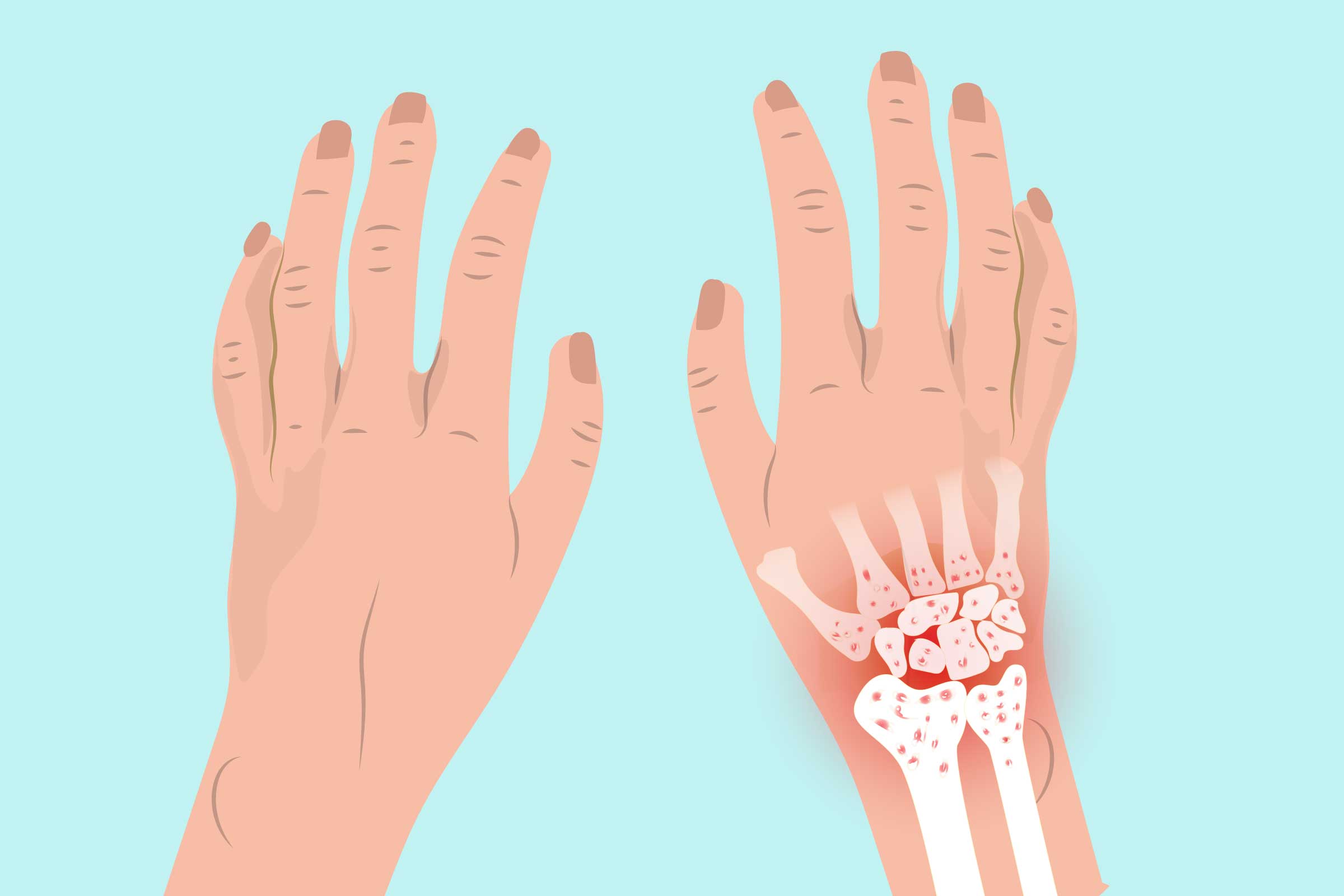
The wrist joint is one of the most important elements of the musculoskeletal system of the human body. This fragile joint is located at the junction of the hands and forearm bones. Most often, this area is subject to injuries, degenerative changes are much less common here. Arthrosis of the wrist joint is a rather rare disease and can greatly reduce a person’s quality of life. Constant loads and injuries provoke degradation of cartilage tissue, which is subsequently accompanied by pain and difficulty in movement. This is how osteoarthritis of the wrist joint develops , causing serious discomfort. Joint mobility is sometimes reduced by half, which causes severe discomfort in the process of performing everyday, habitual manipulations.
Symptoms of arthrosis and osteoarthrosis
It is difficult to recognize these diseases at the initial stages. Patients often do not pay attention to mild pain, and when it becomes strong enough, the disease is already advanced.
- Pain when moving, causing discomfort and serious inconvenience in everyday activities. This is one of the most characteristic symptoms of arthrosis and osteoarthrosis of the wrist joint.
- Pain when trying to lean on the palm, bending the wrist, carrying heavy objects.
- In some cases, edema occurs, and swelling appears in the areas affected by the disease.
- Joint crunching, feeling of limited movement.
Types and degrees of diseases
- Arthrosis and osteoarthrosis of the 1st degree have not very pronounced symptoms and are manifested by minor pain after loads, especially monotonous ones. As soon as the joints return to a state of rest, the pain disappears.
- The development of stage 2 of the disease is accompanied by the appearance of more pronounced problems – pain and discomfort that do not go away for a long time. There is a crunch in the joints, swelling in the phalanges. The patient tries not to make painful movements.
- The third stage is manifested by increased deformations, the appearance of deforming osteoarthrosis, pain at rest, and limited movement. At this stage, the cartilaginous layer is almost completely destroyed, and bone growths may appear along the edges of the joints. Due to decreased motor activity, the muscle tone of the entire arm decreases.
Which doctor should I see?
It is insidious and develops almost without symptoms until it reaches a serious stage. For example, deforming arthrosis can develop as a result of an injury (post-traumatic arthrosis) and not make itself known until serious, difficult-to-treat changes appear. You can contact a therapist, describe the problem and get a referral, or immediately visit a rheumatologist. A dermatologist, urologist, and other specialized doctors can also be involved in solving the problem.
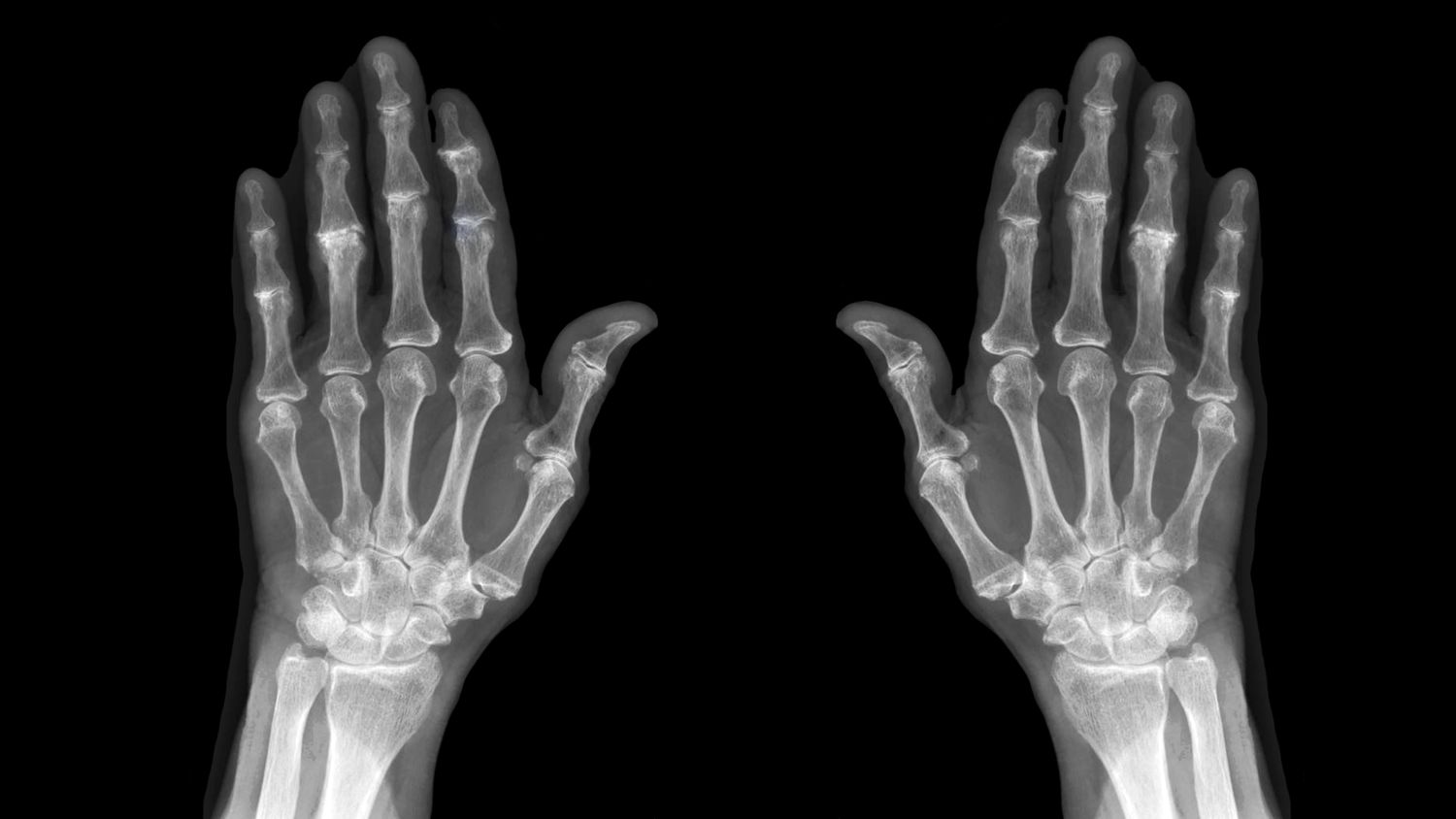
Diagnostics
To make an accurate diagnosis, which is extremely important for successful treatment, a set of diagnostic measures is needed:
- Examination and questioning of the patient at an appointment with an orthopedist.
- Palpation.
- X-ray in two or three projections depending on the clinical picture.
- General tests.
- Ultrasound, CT or MRI if necessary.
- Consultation with other specialists if necessary.
Causes of occurrence
Osteoarthritis can be primary – developing in a healthy joint, or secondary – developing in a joint that has already been affected by some disease. The factors that contribute to the development of deforming osteoarthritis are the following:
- Gender – women are much more susceptible to developing arthrosis of the joints.
- Age-related – after 65 years of age, almost 90% of people have joint pathologies.
- Excess weight, endocrine disorders.
- Excessive strain on the wrist joint. Heavy physical work, professional sports.
- Advanced inflammatory processes in the joints.
- Heredity.
Treatment
In each case, the approach to how to treat the disease may be different. It depends on the degree of the disease, the causes that caused it, the patient’s condition, the damage to the right or left wrist. Among the main methods:
- Exercises, special therapeutic gymnastics.
- Physiotherapy.
- Treatment with medication.
- Maintaining proper nutrition and daily routine.
- Wearing chondroprotectors that help the process of cartilage tissue restoration.
- Taking medications and injections to help restore cartilage.
When the disease reaches an advanced stage, the only way to help the patient is through surgery and prosthetics.
It is important to understand that this disease is chronic, which means that treatment procedures will have to be carried out constantly. However, the earlier osteoarthritis of the wrist joint is diagnosed, the more timely the therapy will begin and the destructive changes in the cartilage tissue will be less. This determines the importance of contacting an orthopedist at the slightest signs of pathology in the joint area.
Recovery
Recovery is aimed at returning motor activity and joint functions. Rehabilitation mainly consists of performing gymnastics, therapeutic exercises, and establishing a balanced nutrition system. Wearing fixing bandages and dressings to speed up the restoration of cartilaginous tissue also gives good results.
To prevent deforming osteoarthritis and other similar diseases – maintain normal body weight, avoid heavy loads, pay close attention to changes in health.