Timings
Evercare Hospital Lahore
- Monday - Thursday (11 am - 01 pm)(07 pm - 09 pm)
- Friday (02 pm - 05 pm)(07 pm - 09 pm)
- Saturday (04 pm - 06 pm)
Contact Info
- Phone: 03060603646
- Whatsapp: 03060603646
- Email: Info@drwaqasjavedorthopedics.com
Nerve Entrapment
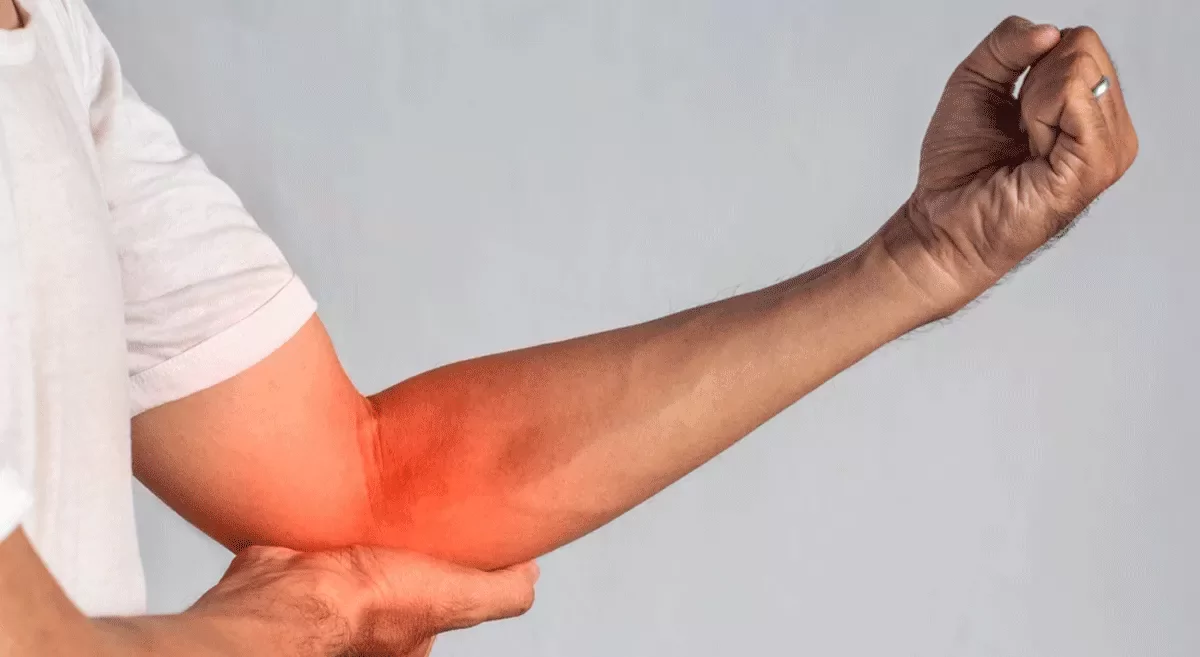
Nerve entrapment syndromes around the elbow and hand are common conditions that can cause pain, numbness, and weakness in the affected areas. These conditions occur when a nerve is compressed or pinched, often leading to discomfort and functional impairment. Understanding these conditions is crucial for effective management and treatment.
Anatomy of Nerve Entrapment
Nerves travel through various tunnels and passages in the body. When these passages become narrowed due to inflammation, injury, or other factors, nerves can become entrapped. In the elbow and hand, the most commonly affected nerves are the ulnar, radial, and median nerves.
Common Types of Nerve Entrapment
- Cubital Tunnel Syndrome:
- Entrapment of the ulnar nerve at the elbow.
- Symptoms include numbness or tingling in the ring and little fingers, elbow pain, and weakness in the hand.
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome:
- Compression of the radial nerve near the elbow.
- Causes pain in the forearm and difficulty in extending the wrist and fingers.
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome:
- Compression of the median nerve at the wrist.
- Characterized by numbness, tingling, and pain in the thumb, index, middle, and part of the ring finger.
- Guyon’s Canal Syndrome:
- Entrapment of the ulnar nerve at the wrist.
- Symptoms include numbness and tingling in the ring and little fingers, and sometimes loss of grip strength.
Symptoms of Nerve Entrapment
- Numbness or tingling in the affected fingers.
- Pain in the elbow, forearm, wrist, or hand.
- Weakness in the hand or fingers.
- Difficulty in performing tasks that require fine motor skills.
Diagnosis of Nerve Entrapment
- Clinical examination focusing on the affected area.
- Nerve conduction studies and electromyography (EMG) to assess nerve function.
- Imaging studies, such as MRI or ultrasound, may be used in some cases.
Treatment Options
- Conservative Management:
- Rest and avoidance of activities that exacerbate symptoms.
- Physical therapy to strengthen and stretch the affected areas.
- Splinting or bracing to immobilize the affected nerve.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for pain relief.
- Surgical Treatment:
- Considered when conservative measures fail.
- Procedures vary depending on the nerve and location of entrapment.
- Common surgeries include nerve decompression and transposition.
Recovery and Management
- Recovery time varies depending on the severity of entrapment and the treatment approach.
- Post-treatment rehabilitation is vital for regaining strength and flexibility.
- Ergonomic adjustments in daily activities and workspaces can help prevent recurrence.
Importance of Early Intervention
Timely diagnosis and treatment of nerve entrapment syndromes are essential to prevent permanent nerve damage and loss of function. Patients experiencing symptoms should seek medical advice promptly. Adhering to treatment plans and engaging in preventive measures can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life.

Conditions I Treat

- Knee Injuries
- Orthopedic Infections
- PCL Injuries
- Multi-ligament Injuries
- Joint Replacement
- Kneecap Dislocations
- Knee Replacement
- Sport Injuries of Knee
- Lower Limb Fractures
- Hip Injuries
- Hip Replacement
- Back Pain
- Shoulder, Elbow, Wrist
- Upper Limb Fractures
- Neck Pain