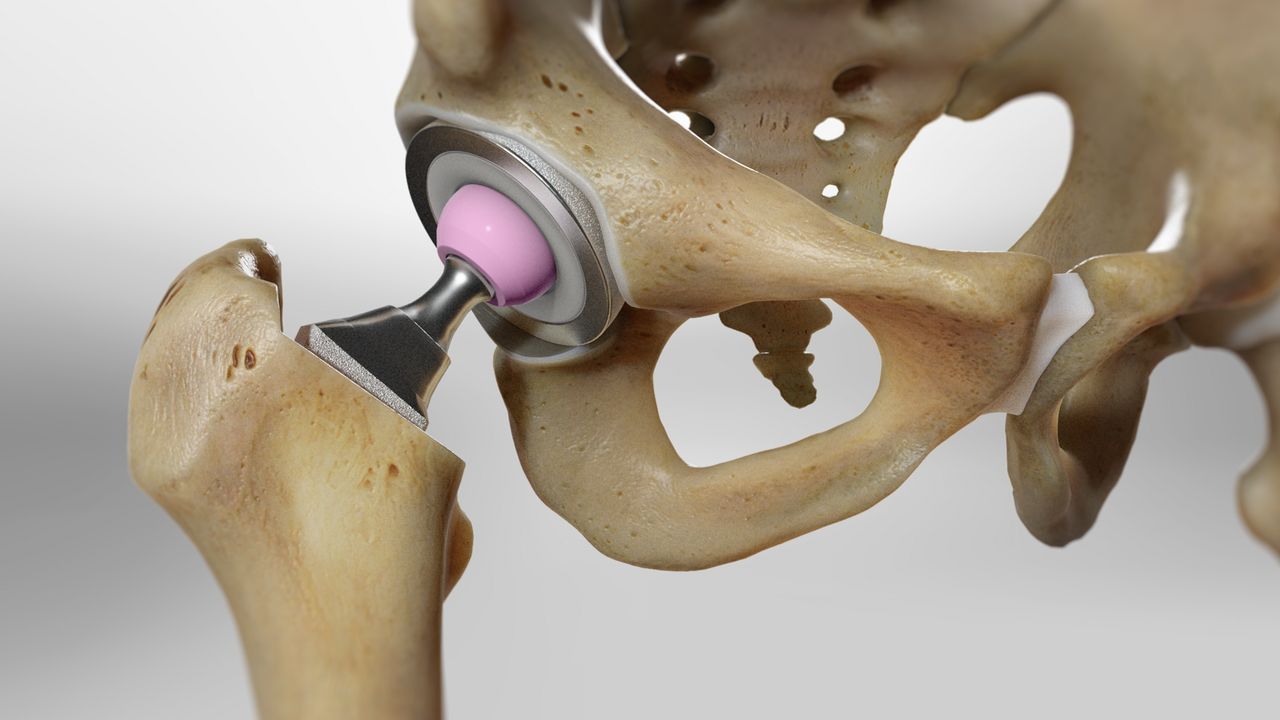
Hip replacement is an effective and often the only way to restore lost limb function. Total, i.e. with replacement of all components of the joint, endoprosthetics is the method of choice in the treatment of:
- Bechterew’s disease (with predominant damage to the hip joints)
- degenerative-dystrophic diseases (arthrosis-arthritis)
- rheumatoid polyarthritis
- aseptic necrosis of the femoral head
- pseudoarthrosis of the femoral neck and non-union of femoral neck fractures
What should a patient know about endoprosthetic surgery?
This is a very precise surgical intervention, the purpose of which is to return you to a mobile, painless joint, allowing you to return to your normal life.
The development of technical progress has led to the emergence of materials that can replace a worn-out joint with an artificial one. Just like a normal hip joint, an artificial one consists of a round head and a concave socket in which the head rotates, allowing for a normal range of motion. For each specific case, an appropriate prosthesis is selected.
Consultation
During the consultation, the doctor will determine the indications and contraindications for hip replacement, conduct the necessary examinations and select the appropriate prosthesis. An X-ray examination will help determine the degree of wear of the joint and make the necessary measurements. You will definitely be warned about the possible risks and complications of the operation. The following complications may be considered:
- infection in the surgical area
- bleeding during or after surgery
- thromboembolism (blockage of a vessel by a blood clot)
- development of pneumonia
- dislocation of the prosthesis, which will require an increase in the treatment period
Before the operation
Before the operation, the patient undergoes a full clinical examination (tests, specialist consultations, anesthesiologist examination). The patient is hospitalized 1-2 days before the operation.
Operation
Hip replacement is a complex surgical intervention that requires high professionalism of the surgeon. In standard cases, implantation of an artificial joint lasts 2-3 hours. During the operation, measures are taken to prevent infectious complications, if necessary, to replenish blood loss, and to drain the wound to prevent blood accumulation.
After operation
In the postoperative period, antibiotics, painkillers, and symptomatic treatment continue. A bolster is placed between the legs to hold the operated limb in the correct position.
Inpatient rehabilitation
Activation in bed is permitted as early as the first day after surgery. From the second day, you can sit up in bed, start static exercises for the limb muscles, and do breathing exercises. Walking with a measured load on the operated limb and additional support (crutches, arena) is possible as early as the third day. The stitches are removed on the 10th-12th day.
Discharge home
Discharge is made 10-12 days after the operation. It is necessary to continue rehabilitation measures, strictly following the recommendations of the operating surgeon. If necessary, hospitalization in a rehabilitation center for recovery under the supervision of rehabilitation specialists is possible. Restrictions on physical activity on the operated limb should be observed for 6-8 weeks after the operation, during this time it is recommended to use additional support.